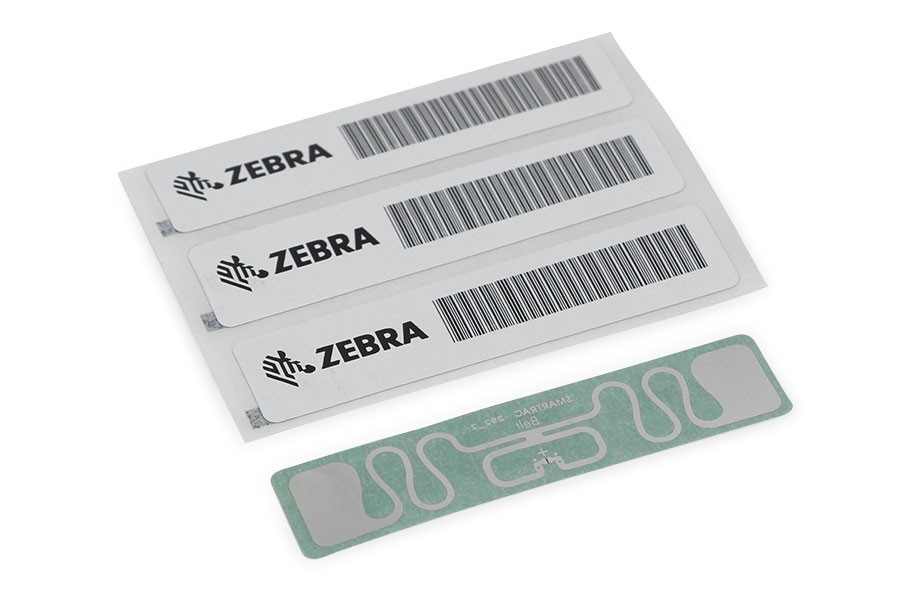
Selecting the Right RFID Tags
RFID labels and tags are the foundation of every RFID solution. They receive RF signals from antennas and readers and relay specified information about a tagged item to your back-end system. RFID tags can either be active or passive. Active tags have their own battery power source, which allows them to broadcast a signal to a reader. Conversely, passive tags have no power source and only get read when they are within the range of an RF signal from a reader. Due to their affordability and versatility, passive tags are deployed in most RFID applications. On the other hand, active tags are often used for high-value asset tracking and real-time location solutions.

Comparing Passive & Active RFID Tags
Passive
Passive tags have no power source. The signal from an RF reader is bounced off of the passive tag and sent back to the reader. Readers and passive tags can communicate within 20 feet. Passive RFID works well for inventory checkpoints, compliance monitoring, and WIP applications.
Active
Since they are battery-powered, active RFID tags can broadcast their own signal to readers. Therefore, these tags are readable for longer ranges, making them best for tracking more expensive assets that require more frequent location updates.
RFID Tag Form Factors
RFID Pros at RMS Omega perform testing to ensure that your tag works as expected to achieve your goals. Different form factors affect the performance of the tag in each application:
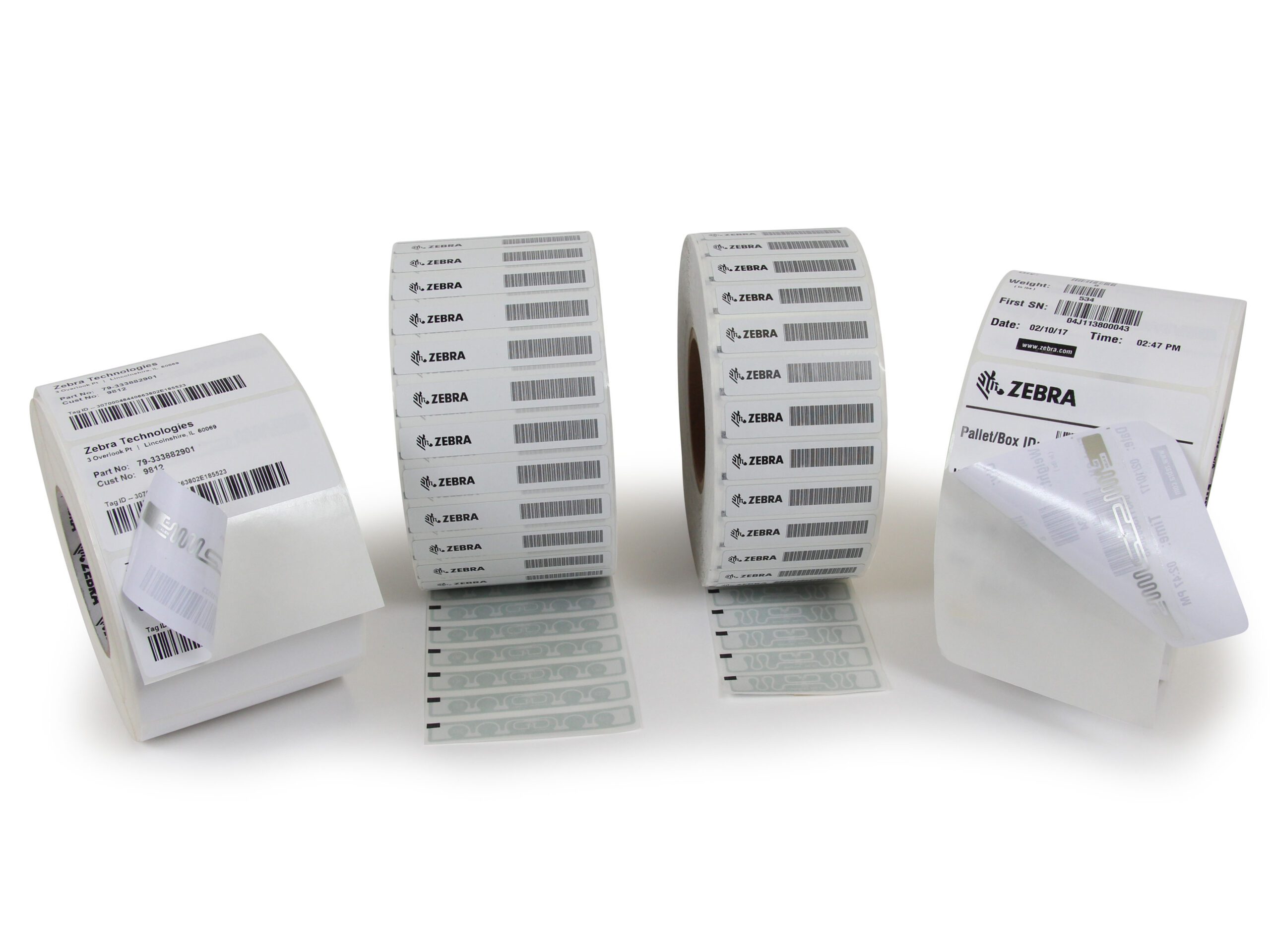
- Inlays – An inlay consists of the RFID chip and tag antennae on a piece of film with an optional adhesive.

- Labels – RFID labels are designed for peel-and-stick applications and are versatile enough to tackle most applications.
- Hard Tag – Encased hard tags protect RFID inlays in challenging environments or outdoor applications.
- Wristband – RFID-encoded wristbands are useful in healthcare for the seamless and instantaneous collection of patient information.
- Card – RFID technology embedded in plastic cards can be used for access control and other applications.
Factors That Impact RFID Tag Performance
Certain factors will impact what RFID tags you should use. A few factors that affect RFID read performance include:
- Inlay size – A larger RFID inlay gives you longer read ranges.
- Frequency – Tags and readers operate at different frequencies that react differently to read range and environmental factors.
- Material surface – The surface of the tagged item and the environment it passes through affect the tag’s accuracy and durability.
- Environmental factors – High metal, carbon, and fluid concentrations can impact tag performance.
RFID Tag Frequencies
There are three common different frequencies at which RFID tags operate. Each frequency band has its advantages and limitations, influencing factors such as read range, interference, and the types of materials the RFID signals can penetrate. The effectiveness of each frequency will depend on your tracking requirements and operating environment.
- Low Frequency (LF) – LF RFID is commonly used for short and mid-range applications, such as access control, and close proximity asset and inventory location. This frequency level is affected less by interference from metal or water.
- High Frequency (HF) – HF RFID is used for short-range communication and fast data transfer speed for access control, NFC, and short-range asset tracking or patient ID.
- Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) – UHF is used in longer-range applications in logistics and supply chain management. These tags are well-suited for inventory scanning at dock doors and on warehouse racking.